Liraglutide Anti-Diabetics for Blood Sugar Control CAS NO.204656-20-2
Product Detail
| CAS | 204656-20-2 | Molecular Formula | C172H265N43O51 |
| Molecular Weight | 3751.20 | Appearance | White |
| Storage Condition | Light resistance, 2-8 degree | Package | Aluminum foil bag/vial |
| Purity | ≥98% | Transportation | Cold Chain and cool storage delivery |
Ingredients of Liraglutide
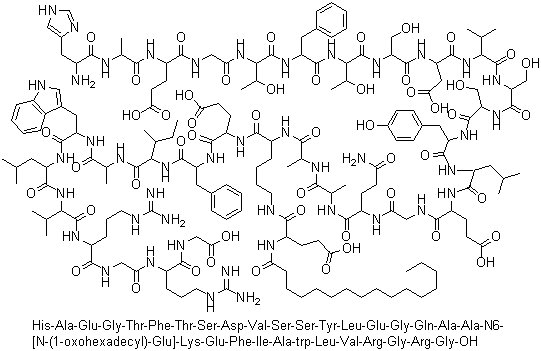
Active Ingredient:
Liraglutide (analog of human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) produced by yeast through genetic recombination technology).
Chemical Name:
Arg34Lys26-(N-ε-(γ-Glu(N-α-hexadecanoyl)))-GLP-1[7-37]
Other Ingredients:
Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate Dihydrate, Propylene Glycol, Hydrochloric Acid and/or Sodium Hydroxide (as pH Adjusters Only), Phenol, and Water for Injection.
Application
Type 2 diabetes
Liraglutide improves control of blood glucose. It reduces meal-related hyperglycemia (for 24 hours after administration) by increasing insulin secretion (only) when required by increasing glucose levels, delaying gastric emptying, and suppressing prandial glucagon secretion.
It is suitable for patients whose blood sugar is still poorly controlled after the maximum tolerated dose of metformin or sulfonylureas alone. It is used in combination with metformin or sulfonylureas.
It acts in a glucose-dependent manner, meaning it will stimulate insulin secretion only when blood glucose levels are higher than normal, preventing "overshoot". Consequently, it shows negligible risk of hypoglycemia.
It has the potential for inhibiting apoptosis and stimulating regeneration of beta cells (seen in animal studies).
It decreases appetite and inhibits body weight gain, as shown in a head-to-head study versus glimepiride.
Pharmacological Action
Liraglutide is a GLP-1 analog with 97% sequence homology to human GLP-1, which can bind to and activate the GLP-1 receptor. The GLP-1 receptor is the target of native GLP-1, an endogenous incretin hormone that promotes glucose concentration-dependent insulin secretion from pancreatic β cells. Unlike native GLP-1, the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of liraglutide in humans are suitable for a once-daily dosing regimen. After subcutaneous injection, its mechanism of prolonged action includes: self-association that slows absorption; binding to albumin; Higher enzyme stability and thus longer plasma half-life.
The activity of liraglutide is mediated by its specific interaction with the GLP-1 receptor, resulting in an increase in cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Liraglutide stimulates insulin secretion in a glucose concentration-dependent manner, while reducing excess glucagon secretion in a glucose concentration-dependent manner.
Therefore, when blood glucose rises, insulin secretion is stimulated, while glucagon secretion is inhibited. In contrast, liraglutide reduces insulin secretion during hypoglycemia without affecting glucagon secretion. The hypoglycemic mechanism of liraglutide also includes a slight prolongation of gastric emptying time. Liraglutide reduces body weight and body fat mass by reducing hunger and energy intake.









