Tirzepatide is a novel dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist developed. Its dual mechanism aims to enhance insulin secretion, suppress glucagon release, delay gastric emptying, and improve satiety, offering a comprehensive therapeutic approach for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity.
Key Findings from Clinical Studies
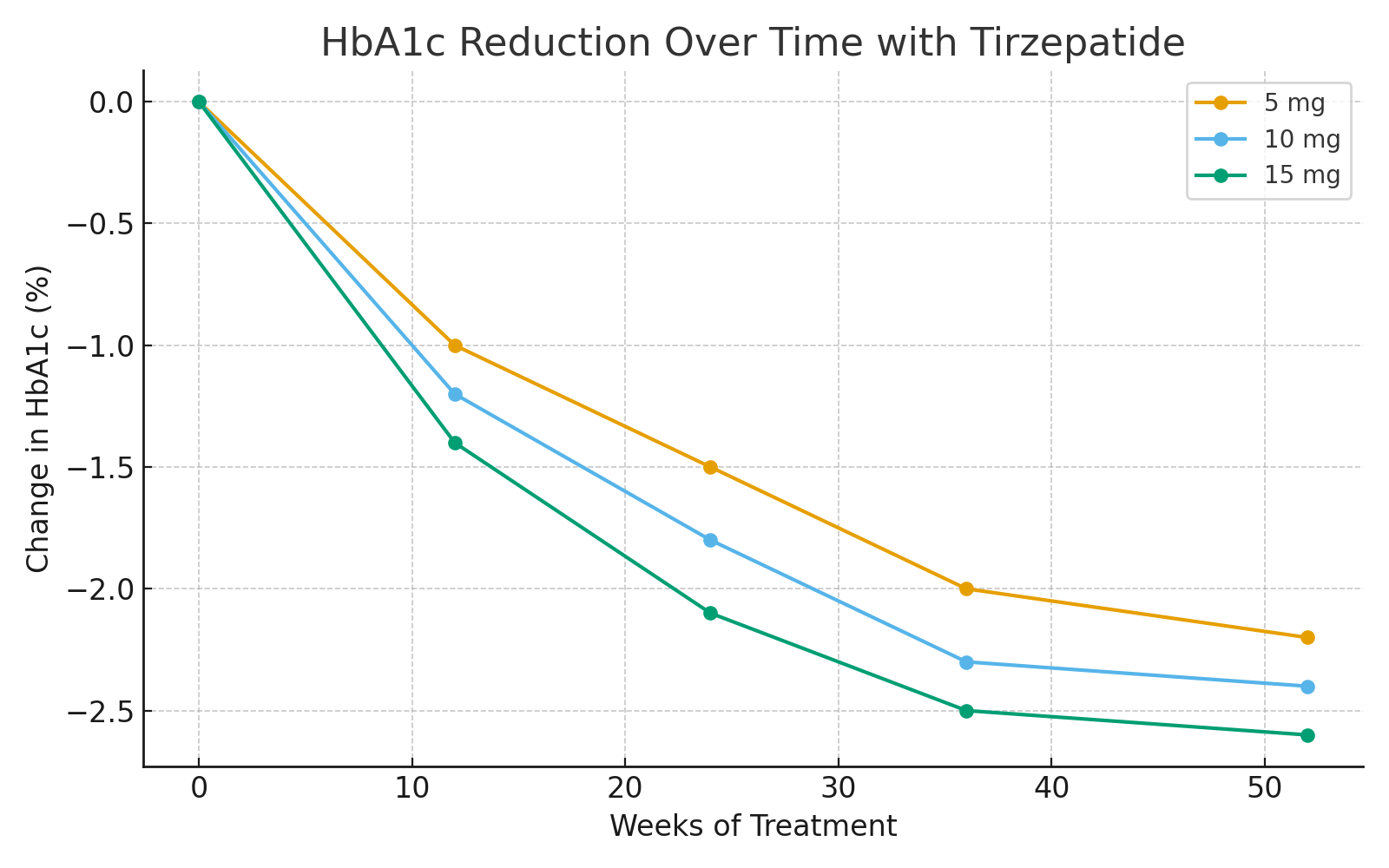
1. Glycemic Control
Across multiple SURPASS phase 3 clinical trials, tirzepatide demonstrated superior glycemic control compared with existing antidiabetic agents, including semaglutide and insulin degludec.
-
Mean HbA1c reduction: up to −2.4% from baseline after 40–52 weeks.
-
A higher proportion of participants achieved HbA1c < 6.5%, meeting or surpassing ADA targets.
-
Significant improvements in fasting plasma glucose and postprandial glucose levels were observed.
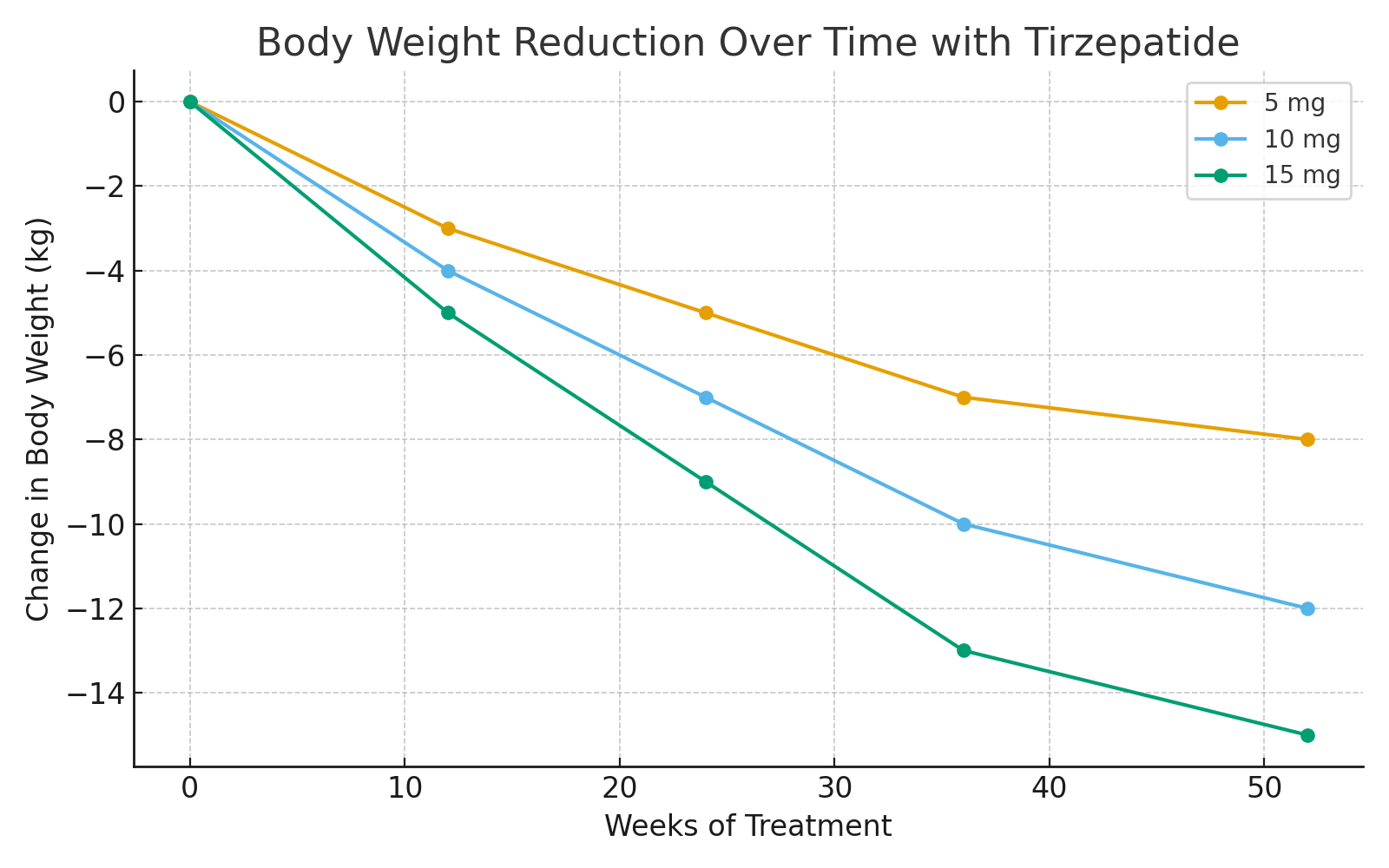
2. Weight Reduction
Tirzepatide consistently produced clinically meaningful and dose-dependent weight loss in both diabetic and non-diabetic populations.
-
In T2DM patients: average body weight reduction ranged from 7–12 kg.
-
In non-diabetic obese subjects (SURMOUNT-1 trial):
-
10 mg and 15 mg doses led to 15–22% mean body weight loss, comparable to or exceeding bariatric surgery thresholds.
-
-
Most participants achieved at least 5–10% weight reduction.
3. Cardiometabolic Improvements
Tirzepatide treatment also improved broader metabolic parameters:
-
Reductions in triglycerides, LDL-C, and total cholesterol.
-
Increases in HDL-C.
-
Significant decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
-
Improvement in insulin sensitivity and β-cell function.
4. Safety and Tolerability
The safety profile was consistent with other incretin-based therapies:
-
Most common adverse events: mild-to-moderate gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea).
-
Low incidence of hypoglycemia, mainly when used with insulin or sulfonylureas.
-
No major safety concerns observed in cardiovascular outcomes.
5. Mechanistic Insights
Tirzepatide’s unique dual receptor agonism amplifies both GIP and GLP-1 pathways:
-
GIP activation enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion and may improve adipose tissue metabolism.
-
GLP-1 activation promotes appetite suppression and delays gastric emptying.
-
Their synergistic effect leads to improved glucose control with enhanced weight reduction compared to single-pathway agents.
Conclusion
Tirzepatide represents a breakthrough in metabolic therapy, providing unprecedented efficacy in both glycemic control and weight reduction for individuals with type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Its dual incretin mechanism offers an integrated approach addressing the root causes of metabolic dysfunction — hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and excess body weight.
Given its robust efficacy and manageable safety profile, tirzepatide may redefine the therapeutic paradigm for diabetes and obesity management in the coming decade.
References
-
Frias JP et al., New England Journal of Medicine, 2021.
-
Jastreboff AM et al., New England Journal of Medicine, 2022 (SURMOUNT-1).
-
Ludvik B et al., Lancet, 2021.
-
Eli Lilly Clinical Data, SURPASS Trials 1–5.
Post time: Oct-04-2025